Defeat of Houston LGBT-rights measure may have broad impact
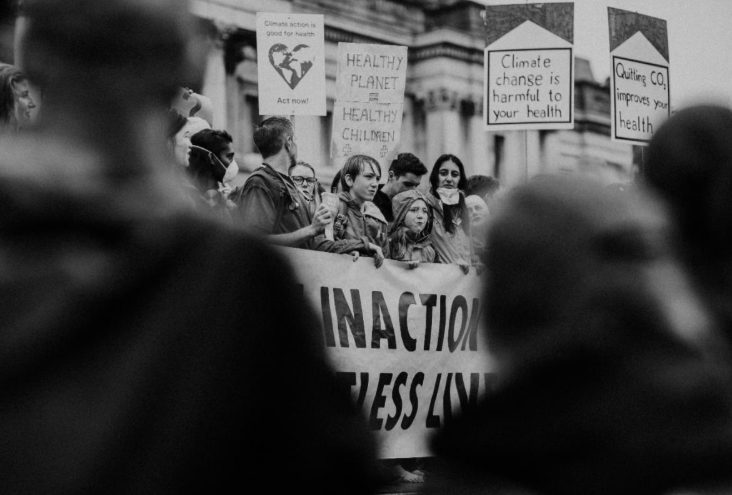
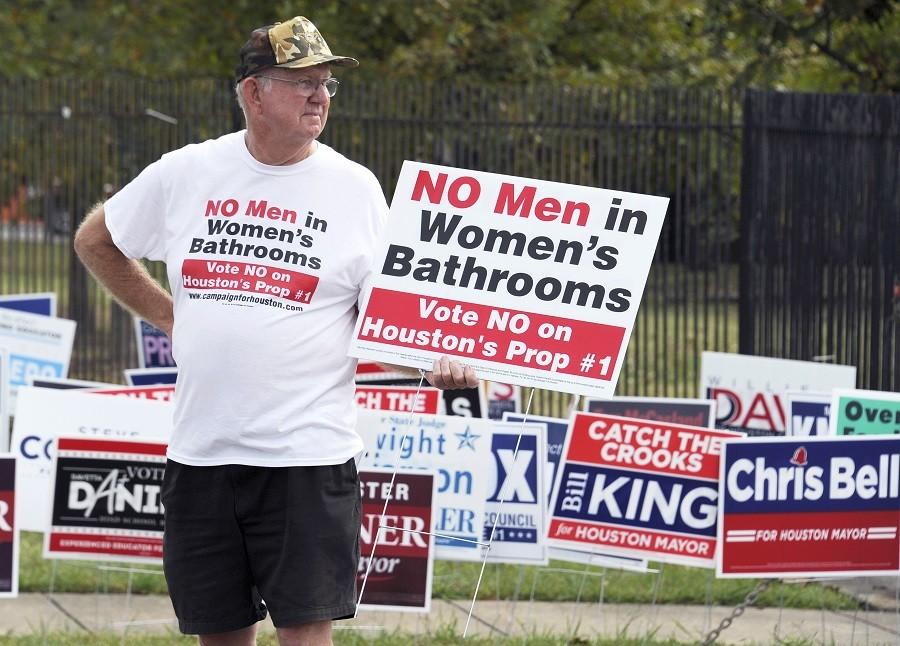
In this Oct. 21 photo, a man urges people to vote against the Houston Equal Rights Ordinance outside an early voting center in Houston. On Tuesday, Nov. 3, voters statewide can give themselves tax breaks, pump billions of dollars into roads and make hunting and fishing constitutional rights by supporting seven amendments to the Texas Constitution on Tuesday’s ballot. And Houston will choose a new mayor and decide whether to extend nondiscrimination protections to its gay and transgender residents in a referendum being watched nationally.
November 4, 2015
HOUSTON — The landslide defeat of a nondiscrimination ordinance in Houston has stunned LGBT-rights activists across the nation. They’re now bracing for their opponents in other states to seize on the successful tactic of stoking fears over transgender people’s access to public restrooms.
By a 61-to-39-percent margin, voters in America’s fourth largest city on Tuesday rejected a broad equal-rights ordinance — extending protections in employment, housing and public spaces on the basis of race, sexual orientation, gender identity and other categories. Opponents prevailed with a campaign that dubbed the measure “the bathroom ordinance” and raised the specter of male sexual predators invading women’s restrooms.
The outcome was “a devastating blow to equality,” said the Human Rights Campaign, a national group advocating for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender people.
“It’s almost unbelievable that this could happen in a city like Houston,” said the campaign’s president, Chad Griffin. “But make no mistake: If we don’t double down today, we’ll face the same thing again and again in cities across the nation.”
The ordinance lost despite strong support from many major businesses, and despite its supporters’ arguments that serious problems with bathroom access have been virtually nonexistent in the 17 states and scores of cities that have banned discrimination against transgender people in public accommodations.
“This is a national game-changer,” said Jonathan Saenz of Texas Values Action, which opposed the ordinance. He described the result as “a massive victory for common sense, safety, and religious freedom.”
The outcome in Houston was swiftly seized upon by opposing sides in California, where the legislature passed a law in 2013 allowing transgender students to participate in activities and use facilities corresponding to their gender identity. Opponents are gathering signatures for a 2016 ballot measure that would overturn the law and require people to use facilities that correspond with their “biological sex.”
Karen England of Privacy for All, which is promoting the ballot measure, noted that in both Houston and California there were efforts to prevent a public vote on the nondiscrimination issue.
“Houston elites were afraid to let the voters vote, and they had good reason to be,” England said. “We think California elites have similar reason to be afraid.”
England’s group and its allies are seeking to collect 500,000 signatures by Nov. 20 to ensure they have enough valid signatures to qualify for the November 2016 ballot.
A coalition of gay-rights supporters who back California’s 2013 law warned that the state may face a campaign echoing the one in Houston.
“We fully expect our opponents to use the same misinformation and scare tactics in California that they used in Houston,” said Rick Zbur, executive director of Equality California. “Since they can no longer stop same-sex couples from getting married, this is the next page in their attempts to discriminate against the LGBT community.”
In Houston, there was some second-guessing on Wednesday as to whether supporters of the ordinance — including the lesbian mayor, Annise Parker — could have mounted a more effective campaign.
Robert Stein, a political scientist at Rice University, said the campaign failed to counteract the “bathroom ordinance” message with arguments that might have better resonated with voters, particularly African-Americans who turned out in large numbers.
Stein said voters might have supported the ordinance if persuaded that its defeat could mean potential economic losses, including companies deciding not to relocate to Houston or organizations deciding not to hold meetings or conventions in the city.
Ordinance supporters, including the Greater Houston Partnership, an influential business group, had warned that defeat of the measure might trigger economic boycotts or endanger plans for Houston to host the Super Bowl in 2017 or the NCAA Final Four in 2016. But the message that supporters pushed in advertising focused mainly on protections against discrimination.
“They had allies in the African-American community, who are traditionally Democratic and progressive voters but did not buy into the argument that gays and more specifically transgender (people) are a group that needs to be protected,” Stein said.
Parker, who is completing her third and final term, described the result as “sad for Houston.”
“I fear this will have stained Houston’s reputation as a tolerant, welcoming, global city,” she said. “And I absolutely fear that there will be a direct, economic backlash as a result of this ordinance going into defeat.”
The NFL said the ordinance’s defeat will not affect plans for the 2017 Super Bowl.
“We will work closely with the Houston Super Bowl Host Committee to make sure all fans feel welcomed at our events,” the NFL said. “Our policies emphasize tolerance and inclusiveness, and prohibit discrimination based on age, gender, race, religion, sexual orientation, or any other improper standard.”
Nationally, nondiscrimination laws have become the LGBT-rights movement’s top priority now that same-sex marriage is legal in every state.
A proposed federal nondiscrimination law is given no chance of passage any time soon because of Republican opposition, so activists are waging local and state-level campaigns. Frequently, the most visceral issue that arises is transgender people’s access to public restrooms, and in some cases public schools have become the battleground.
In Palatine, Illinois, for example, school officials are at odds with the U.S. Education Department after being told they’re violating federal law by denying a transgender student unrestricted access to a girls’ high school locker room. In Wisconsin, some Republican lawmakers have introduced a bill that would bar transgender students from using the locker room or bathroom assigned to the gender with which they identify.
____
Crary reported from New York